5 Stages of the ITIL Service Lifecycle: A Simple Guide to Better IT Service Management
ITIL suggests these 5 stages as a basis for your ITSM processes. Let’s find out how it can be helpful for you.
ITIL suggests these 5 stages as a basis for your ITSM processes. Let’s find out how it can be helpful for you.
In IT service management, the ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) service lifecycle has become a well-known and effective way to deliver high-quality IT services. This article will explain the ITIL service lifecycle, its benefits, and how it can be used in real-life situations.
Whether you work in IT or are a business leader looking to improve your organization’s IT service management, understanding the ITIL lifecycle is essential for success.
Table of contents:
The ITIL v3 is largely based on the service lifecycle concept.
ITIL v3 defines the service lifecycle as “an approach to IT service management that emphasizes the importance of coordination and control across the various functions, processes and systems necessary to manage the full lifecycle of IT services.”
Here are the five stages of the service lifecycle:
The Service Strategy stage is the foundation of the ITIL lifecycle. It focuses on defining IT services’ overall direction and goals and ensuring that they align with the organization’s business objectives. This stage involves identifying customer needs and determining the services that the IT service provider will offer to meet those needs.
This lifecycle stage involves:
Read about the ITIL framework in our other articles:
Service Design is the stage where the great ideas and goals from Service Strategy are turned into a concrete plan. It’s like being an architect—creating detailed blueprints to make the vision for a building a reality.
In this stage, the focus is on designing IT services that will meet the business’s needs. It’s all about ensuring that the services actually support the organization’s objectives.
Some of the key activities in Service Design include:
The Service Transition stage manages the process of moving new or changed services into the live environment. Returning to our construction metaphor, this stage is like the actual construction process, when the building is completed according to the blueprints and is ready to move in.
In this stage, the focus is on ensuring a smooth and controlled transition of services from development to production. It’s all about ensuring the new or changed services are implemented with minimal disruption to the business.
Some of the key things managed in Service Transition include:
The Service Operation stage is about of delivering and supporting IT services on a day-to-day basis.
In this stage, the focus is on maintaining the performance and availability of IT services and ensuring that users can access and use those services as needed. It’s all about keeping the lights on and the engines running.
Key responsibilities of Service Operation include:
The Continual Service Improvement (CSI) stage is an essential component of the ITIL framework, focusing on the ongoing monitoring, measurement, and improvement of IT service quality. This stage is designed to ensure that IT services continue to meet the evolving needs of the business and deliver value over time.
The key objectives of the CSI stage include:
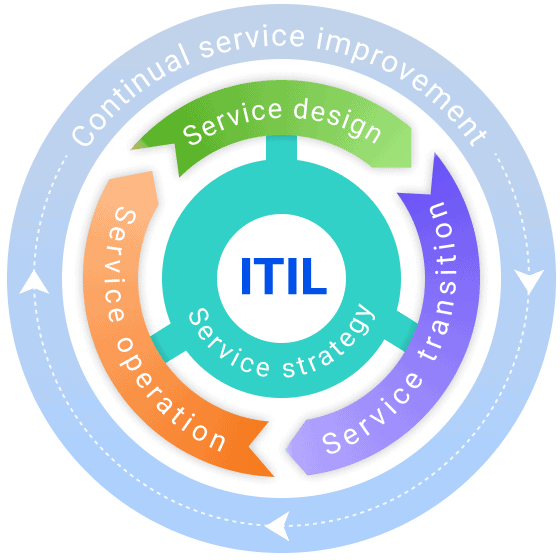
The typical visual representation of the ITIL lifecycle stages
The ITIL service lifecycle has many benefits for modern IT service management:
Alloy Navigator® is an ITIL-based software suite for IT Service Management and IT Asset Management designed and built with industry best practices and real-world customers in mind. It equips you with the tools to streamline and improve the efficiency of ITIL processes, such as Incident Management and Problem Management, Change Management, Knowledge Management, and more.
Here are our key strengths:
Connect with our sales team if you want to bring our product home!
You can explore different ITSM solutions in our article on the Best ITSM tools.
Back to other tips for implementing the ITIL service lifecycle:
ITIL 4 introduces the Service Value System (SVS), which builds on the service lifecycle by adding new elements like the Four Dimensions model and the Service Value Chain. While the SVS doesn’t replace the service lifecycle, it provides a more complete approach to IT service management.
Organizations currently using ITIL v3 can benefit from moving to ITIL 4, as it offers a more flexible and adaptable framework for managing IT services in today’s complex and fast-paced digital world. To ensure a smooth transition, consider the following steps:
Start your trial with Alloy Software today
By mastering the ITIL service lifecycle and embracing its principles, you’ll be well-prepared to drive success in your organization’s IT service management efforts. Remember, the journey to excellence is ongoing, so stay committed to learning, adapting, and continually improving your IT services.
The service catalog is a key part of the Service Design stage. It provides a complete list of all IT services offered by the organization, along with their details and specifications.
The Service Strategy stage of the lifecycle focuses on understanding and aligning IT services with the organization’s overall goals. This ensures that IT investments support the organization’s objectives.
ITIL 4’s Service Value System builds on the service lifecycle by introducing new elements like the Four Dimensions model and the Service Value Chain. This provides a more complete and flexible approach to IT service management.
Organizations can measure success by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as service availability, incident resolution time, customer satisfaction, and cost savings. Regular reporting and analysis of these metrics can show the value of the ITIL service lifecycle and identify areas for continuous improvement.